The 5 Best Ways to Learn JavaScript Fast (For Beginners)

It might be hyperbole to say that JavaScript is a developer’s best (digital) friend — but it would certainly be hard to get by without it.
According to a recent survey conducted by Stack Overflow, JavaScript is the world’s most popular programming language, with an incredible 69.7 percent of the 90,000 developers polled citing it as the most-used skill in their programming toolbox. It’s a staple skill for all manner of developers, from the most entry-level junior developers to the highest-ranked programming specialists.
The 5 Best Ways to Learn JavaScript Fast
The chances of a developer not needing to learn or use JavaScript at some point in their careers are slim to none; even if a job doesn’t require its day-to-day use, applicants still typically need to prove their command over it in the interview stage.
A recent report published by DevSkiller found that not only does the language top the list of the skills developers are tested on during the job search, but that “most developers will get a JavaScript IT skills assessment, regardless of their main focus.” More to the point, a full 72 percent of companies who need developers hire professionals who are proficient in JavaScript.
Like it or not, aspiring developers can’t get away from learning JavaScript. The reason is simple: It’s just too darn useful.
Curious about web development? At The Coding Boot Camp at UT Austin, you’ll learn JavaScript and other programming languages in just 12 or 24 weeks. Complete the form below to learn more.
Get Program Info
What is JavaScript, and Why Should You Learn It?
Let’s break this down. JavaScript is typically used as a client-side scripting language for front end development. In simple terms, this means that developers use JavaScript to build the part of a website that ordinary visitors can see and interact with, also known as the “front end.” While the programming language can technically be used to create complex programs, its primary application lies in web development.
Front end programmers typically use JavaScript in conjunction with two markup languages, HTML and CSS, to create all of the elements that a user can see and interact with directly. Most common actions, such as transactions, submitting customer feedback, and even logging in, are facilitated by HTML code. CSS, on the other hand, centers more on formatting and appearance; it allows developers to describe how the HTML should look to a visitor. Both, however, are static. With only HTML and CSS, a web page is unchanging and relatively simplistic.
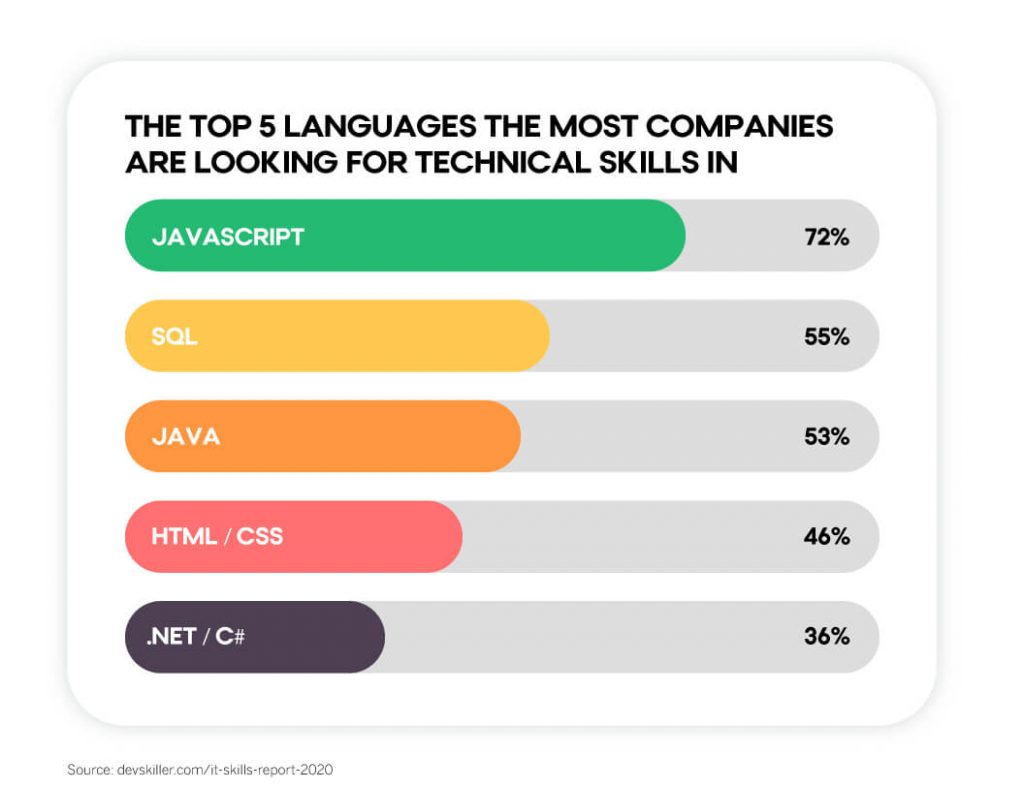
With JavaScript, a website becomes dynamic. Not only does it automate processes that users would, in an HTML-only site, need to perform manually, but it also empowers a website to react to a visitor’s input. Autocorrect functions, slideshows, interactive graphics: these can all be credited to JavaScript working tirelessly in the background.
That said, JavaScript’s appeal isn’t confined to its functionality. It’s also one of the most intuitive programming languages to learn and use; often, it’s one of the first that newbie developers learn when they start to code.
“JavaScript is very easy to implement,” writes one tech journalist for Web Platform. “All you need to do is put your code in the HTML document and tell the browser that it is JavaScript […] then, JavaScript allows you to create highly responsive interfaces that improve the user experience and provide dynamic functionality, without having to wait for the server to react and show another page.” It’s fast, versatile, and can even help identify and fix problems via its browser support functions.
For those reasons, JavaScript maintains a significant presence in the development sector and is a valuable skill for any aspiring web programmer. If you’re interested in growing your technical skill set, you should take the time to learn the language. Becoming a front end developer may take as little as 3 months.
Luckily, it isn’t all that hard to hone your skills. There are countless ways to learn JavaScript easily — and no, you don’t need to enroll in an undergraduate computer science program to do it. Online courses and self-led tutorials abound. If you want more structure and guidance, but don’t have the time or money to dedicate to a formal undergraduate degree, you can even enroll in a coding boot camp.
Below we have listed a few of the best ways to learn JavaScript if you’re a beginner.
The 5 Best Ways to Learn JavaScript Fast
1. Self-Guided Websites and Courses
The Internet is, above all else, a repository of knowledge. Whether you’re interested in self-guided learning or just don’t have the time to enroll in a formal program, flexible online courses might be the educational answer for you. These free and paid online courses show you how to learn JavaScript fast, but do keep in mind that “free” doesn’t always equate to “better.” Often, free programs will have less direction and offer less support than their paid alternatives. Be sure to do your research before you take your first class!
Introduction to JavaScript
- Offered by: FreeCodeCamp
- Free
- This course is intended for aspiring programmers who have little to no prior knowledge of JavaScript. Its classes conduct deep dives into web scripting, data types, and JavaScript objects and loops. This course also offers a coding test after each unit to provide students with a means to demonstrate and reinforce their technical knowledge.
Intro to JS: Drawing & Animation
- Offered by: Khan Academy
- Free
- As the name suggests, this no-cost course teaches students how to create illustrations and animations through simple JavaScript code. It structures its lessons via a host of videos, written guides, and exercises.
JavaScript Guide
- Offered by: Mozilla Development Network (MDN)
- Free
- While it’s not a course per se, MDN’s JavaScript Guide provides comprehensive written tutorials that can walk developers of all experience levels through JavaScript’s capabilities. These guides are organized into four broad sections that target amateurs, beginners, intermediate programmers, and experts, respectively.
Modern JavaScript From the Beginning
- Offered by: Udemy
- Paid
- This paid program provides JavaScript beginners with over 20 hours of on-demand video content and a library of downloadable resources. Students can progress at their own pace and access course material via their computers, mobile devices, or television.
Introduction to JavaScript
- Offered by: Codecademy
- Paid
- This paid program provides an in-depth overview of the foundational elements of JavaScript, including data types and functions, objects, and control flows and loops. It also offers post-lesson quizzes and practical exercises to reinforce knowledge gained during the course.
2. Books
When in doubt, read a book. While countless books can offer practical insights into programming, the titles mentioned below are particularly useful for aspiring programmers who want to learn JavaScript quickly.
JavaScript for Kids
- Nick Morgan
- Don’t let the title fool you. While Nick Morgan’s playful text was written for a young audience, its simplified, easily digestible lessons can be useful for adult learners as well. This text offers clear overviews of foundational explanations of strings, arrays, and loops, as well as more advanced investigations of jQuery and graphic creation. It also provides step-by-step instructions on how to program basic games.
You Don’t Know JS: Up & Going
- Kyle Simpson
- Contrary to what you might have guessed from the title, You Don’t Know JS isn’t a book meant for total beginners. It might apply to them — but it isn’t limited to novices. To borrow a quote from the book’s back flap, “It’s easy to learn parts of JavaScript, but much harder to learn it completely — or even sufficiently — whether you’re new to the language or have used it for years. With the ‘You Don’t Know JS’ book series, you’ll get a more complete understanding of JavaScript, including trickier parts of the language that many experienced JavaScript programmers simply avoid.” This text is the first of a series that similarly covers the technical ins and outs of JavaScript. It includes the “basic building blocks of programming” as well as foundational JavaScript skills.
Eloquent JavaScript: A Modern Introduction to Programming
- Marjin Haverbeke
- This text provides foundational instruction and context to those who have relatively little experience with JavaScript. Its intent: to teach readers “how to write beautiful, effective code.” Haverbeke’s lessons center on the basics of programming, including topics such as syntax, control, data, and functional programming techniques. He also includes step-by-step instructions on how to build dynamic programs such as an artificial life simulation and a paint program.
3. Coding Boot Camps
Maybe the self-taught route isn’t for you. While you know that you could push yourself to learn from an on-demand self-guided course or out of a book’s activity chapters, you want a little more support and guidance throughout your educational journey, as well as a certificate upon completion.
If that’s the case, then a coding boot camp might be the route for you. In recent years, boot camps have come to the educational forefront as a means to gain marketable skills quickly, and without spending the time or money that traditional four-year educational programs require. The average boot camp tends to run between a few weeks and a few months, depending on whether their structure follows a part- or full-time schedule.
This short-term timeline makes a coding boot camp one of the best ways to learn JavaScript fast so you can get right back to work (or look for a more attractive position with your newly acquired skills). This kind of professional course has seen a popularity boom in recent years; according to a 2019 Course Report study, enrollment for virtual boot camp programs grew 171 percent between 2018 and 2019, while the coding boot camp market as a whole grew by 49 percent over the same period.
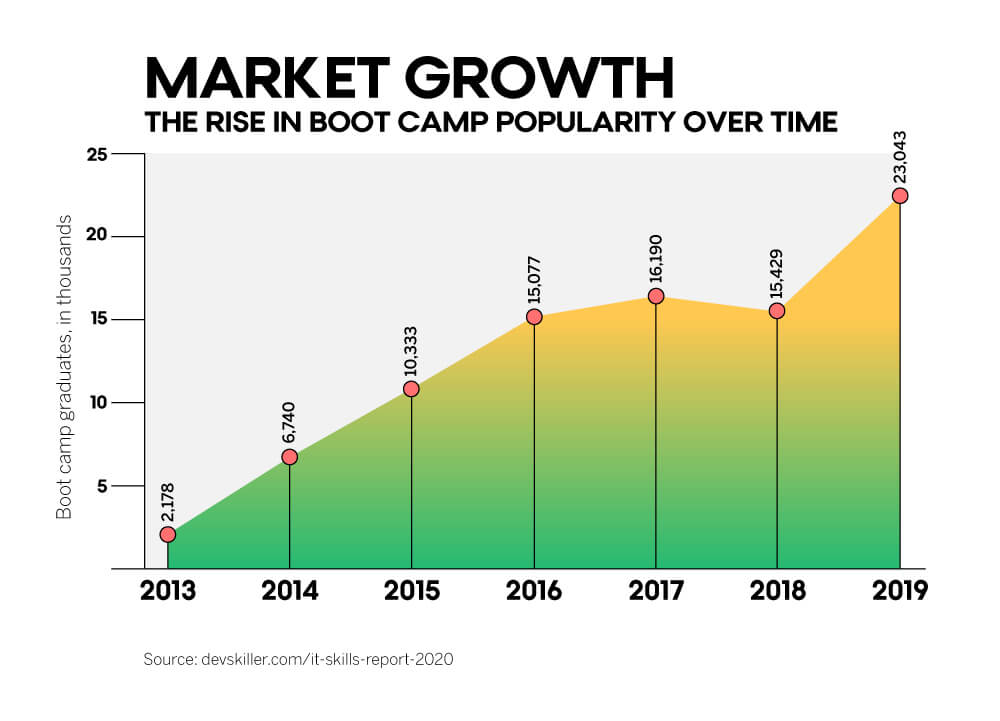
If you’re wondering how to learn JavaScript fast without taking an extended break from work, a coding boot camp may be worth it. It’s challenging to find a boot camp that only teaches one programming language — but if you can pick up other marketable skills as you develop your JavaScript proficiency, why wouldn’t you?
4. Meetups and Networking Events
“Networking” probably isn’t the first (or most conventional) answer that comes to mind when you start researching the best ways to learn JavaScript — but it is among the most useful.
The educational benefits of attending meetups and networking events are considerable. If you’re focused on learning JavaScript quickly, going to panels on the language will allow you to learn from people who have a wealth of experience using it. But the learning doesn’t stop at a presentation; it continues in the conversations you have afterward.
“You may think, ‘I don’t need friends. I’m fine.’ Trust me — this sort of rapport with like-minded peers is exactly what you need,” business and career writer Peter Tourian shared in an article for Forbes. “It feels good to help people and it’s crazy how much you end up learning and receiving just by doing everything you can to assist others.”
Sometimes, the best way to learn JavaScript isn’t to sit with your nose to the grindstone or in a book; it’s to speak with others who are learning, exploring, and achieving with you.
5. Starting Your Own Projects
If you don’t put your hard-earned knowledge into practice, what was the point of learning it in the first place? At some point, aspiring developers need to make the transition from tutorials to real, honest-to-goodness programming. But that shift isn’t always smooth.
It can feel overwhelming to move beyond the comfortable bounds of step-by-step assignments and build an app from scratch. But if you continue to reach for tutorials, you’ll never have the opportunity to exercise your creativity or even take your first step into independent development. The best way to learn how to code is by programming — but you don’t need to launch into a massive project from the get-go to do it.
Start small. When you feel that you’re ready to apply your JavaScript skills to a real project, try adding a feature to a program you created in a tutorial rather than starting another program from scratch. Or, begin within an existing framework and start building Chrome extensions. If you need support, try co-constructing a project with a friend.
The hardest step is always that first effort to remove the tutorial training wheels. Not sure where to start? Try a few of the projects listed below to apply your JavaScript knowledge to a new project!
Build a Drum Kit
With JavaScript, you can build a digital drum set that will allow you to play different sounds according to a home-built keyboard. You can set event-listeners, identify key codes, and sync your JavaScript code with CSS transitions. Follow Varun Barad’s directions on Dev to get started.
Tic-Tac-Toe
Sometimes, the most basic games make for the most useful projects. Follow Ethan Ryan’s instructions on Level Up to create a playable, repeatable game using JavaScript.
HTML Calculator
Create a simple calculator in less than an hour. FreeCodeCamp offers clear instructions on how to think through the creation process, how to write the code, and how to polish your work after you’ve drafted it. Once you’ve walked through the process, you’ll be able to make a decent simulation of a mobile calculator.
No matter how you decide to learn JavaScript, it will take time, effort, and dedication. Whether you’re interested in becoming a front end developer, or are already in the field and just want to add to your professional skill set, there are a number of education options at your disposal. You may find that furthering your career horizons won’t be as challenging — or costly — as you originally thought it would be.

 Live Chat
Live Chat